
Machine learning is another trend in which we are at the moment and supposes that we can take advantage of it to obtain better recommendations when listening to those music playlists on Google Play Music. Yesterday we were commenting on the play of the big G With the new update and that machine learning that will get to know more about you as you use the application more.
Now you want to use that engine for what are all those photographs that are limited by the resolution of the device or by the reduced internal memory of a device. Google does not want to miss the opportunity that is that higher resolution photographs are increasingly needed, because screens, such as smart TVs or phablets, demand them. That is why it has introduced the technique called RAISR.
"RAISR: Rapid and Accurate Super-Resolution Image"
It is a technique that incorporates machine learning in order to produce high-quality versions of low-resolution images. RAISR produces results that are comparable to or better than available super resolution methods, and even improves performance time by 10 to 100 times. This speed in the process allows them to be available on a device in real time. Even later, this technique will prevent the recreation of jagged or aliasing artifacts that exist in low-resolution images.
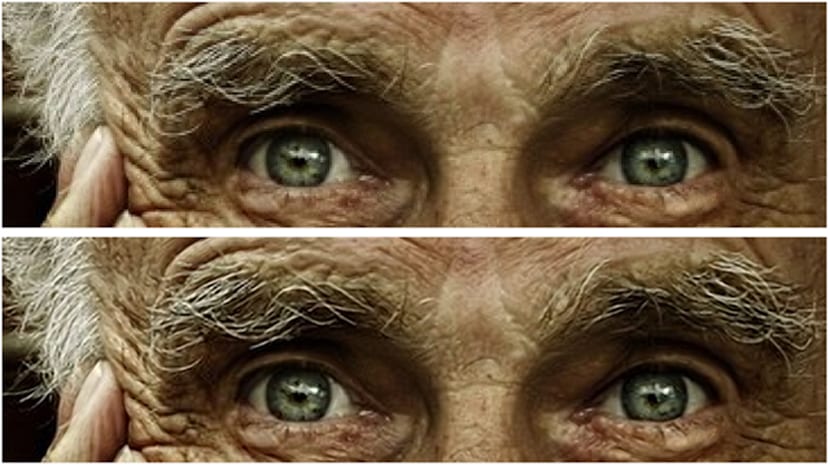
For a few years there has been a technique called upsampling, which produces a larger image with a higher number of pixels and higher image quality from a low resolution one. A technique that uses linear methods that fill in the values of a new pixel by using combinations of the values that surround it. This method is fast because they are linear filters. While what makes them fast does make them less effective at presenting vivid detail in higher resolution results. The image below shows it perfectly.

How RAISR works
RAISR uses the machine learning with a couple of images, one of low quality and one of high quality, to find filters that, when selectively applied to each pixel of the lower resolution image, will recreate details that are comparable to the quality of the original. RAISR can be "trained in two ways." The first is a direct method, in which the filters are learned directly from the pair of low and high resolution images. The other method passes a filter similar to the "upsampler" method to the low resolution image and then "learns" the filters of the given pass and the high resolution image.

Whatever the method, RAISR filters they are "trained" according to the characteristics of the "peaks" found in small patches of images, such as color / brightness gradients, textured or flat regions and more, which are characterized by direction, power and coherence.
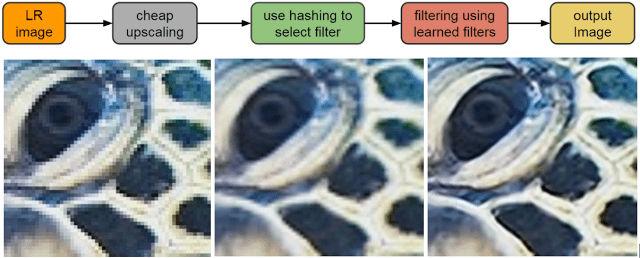
In short, in real time RAISR selects and applies the most relevant filters from the list of those learned from each neighboring pixel in the low resolution image. When those filters are applied to the worst quality image, recreates details that are comparable in quality to the original high resolution. This is what it does is eliminate jagged artifacts like Moire patterns and more.
To this day, the use of machine learning, over decades of advances in imaging technology, has enabled progress in image processing that lies in a wide variety of potential benefits. One of the examples given by Google would be to improve the gesture of «pinch to zoom» or «pinch» on the phone, which would achieve that it could be captured, saved or transmit images in a lower resolution so that it finally arrived at its destination in its proper and high-quality resolution. This would mean a great saving in the data used in the transfer and in the storage plans.